
Antibiotic resistance happens when microbes like bacteria and fungi can defeat the antibiotics designed to kill them. Infections caused by antibiotic resistant germs are difficult to treat, and sometimes impossible. Antibiotic resistance has nothing to do with one’s body resisting the antibiotics, it is entirely the infection, or the pathogen, that has become resistant to the antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance is an upcoming and urgent public health issue because of how severe antibiotic resistant infections can be and how difficult they are to treat. As these antibiotic resistant infections rise in numbers, putting more and more people at risk, making the infection difficult to identify and contain the spread. In 2013, the CDC reported that each year in the US at least two million people get an antibiotic resistant infection, and each year at least 23,000 people die.
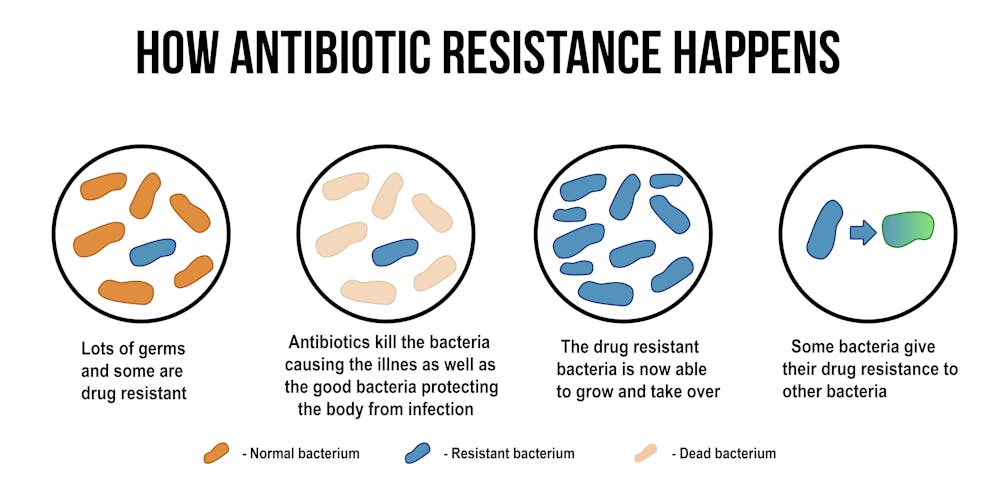
Antibiotic resistance occurs due to genetic mutations in the bacterial DNA. Gene mutation in a bacterial cell can occur in a few ways. The first way is through random mutations. These mutations are not intentional and are typically harmful to the cell cycle of the bacteria. The second way a bacterial cell can generate genetic diversity is through gene transfers. Gene transfers can happen by transformation, transduction, or conjugation. Transformation is the uptake of naked DNA by a competent cell. Transduction is the transfer of DNA by way of bacteriophage. Conjugation occurs when genes on plasmids are transferred from a live donor cell to a live recipient through a sex pilus.
No matter which way a gene transfer occurs, these transfers of genetic material are extremely important in terms of antibiotic resistance. Bacterial cells do not even have to be of the same genera to transfer genes to each other. For example, you may have Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria and Streptococcus pneumoniae present. Now lets assume these two particular bacteria each come with a drug resistant gene. The Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria has gene resistance to Penicillin and the Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria has a genetic resistance to Cefprozil. Once these two bacteria come into contact with each other they may share their resistant genes with each other. We now have an incredibly dangerous bacterial infection because both bacteria contain the genetic material for resistance to multiple antibiotics.
There is a few known causes to antibiotic resistant infections. Abuse and over use of antibiotics in the human population, increased world travel, antibiotic abuse in agriculture, and the lack of knowledge on the subject of antibiotic resistant infections.

Now one may ask, how can antibiotics be abused and over used? Antibiotics can be abused due to how and why antibiotics are prescribed to patients, and patients often not following and completing their prescription as written. Antibiotics should also never be taken for viral infections such as the common cold or influenza. The CDC stresses to healthcare professionals to follow proper guidelines when prescribing antibiotics to patients. Such as, performing the correct diagnostic tests to identify the bacterial infection, prescribing the right drug, the right dose and the right duration of the antibiotic. When following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can ensure that their patients are receiving the correct antibiotic for their infection and that the antibiotic is working correctly to kill off the bacterial infection. If a patient was prescribed an antibiotic that does not successfully kill the bacteria causing the bacterial infection, the bacteria remains in the body and the antibiotic that was prescribed often will kill off all of the "good bacteria" that lives in our body in a mutual symbiotic relationship. Which then allows the body to be vulnerable to the bacteria that is causing the bacterial infection, therefore allowing the infection to worsen.
Issues with antibiotics used in farming have recently come to light. Many farmers overuse antibiotics with the goal to prevent infection within their livestock and feed. However, these antibiotics are often used at sub therapeutic levels. Farmers argue that antibiotic use is keeping and producing their animals in good health and therefore yielding better quality of food. Scientist argue that sub-therapeutic levels of antibiotics are only contributing to drug resistant mutations in bacteria and other microorganisms. This has become a worldwide issue. Developing countries have the greatest amount of use and abuse of antibiotics due to their easy access and over-the-counter availability.
The World Health Organization created a Global Action Plan which demands that each country should develop its own national plan in correspondence to the GAP, in range of its own financial resources and extent of its issue. This is a great first start. However, it also creates another issue, the financial ability to regulate antibiotic use in farming and agriculture. Many countries are already disproportionately affected by inappropriate antibiotic use due to the lack of funding and education available. Since many scientists agree that agricultural life is a great contributing factor to antibiotic resistance, it is important to get everyone involved in this call-to-action plan.

The CDC is currently working on tackling this issue at hand. The CDC has developed what is called the “AR Solution Initiative”. This consists of laboratory tests that can aide and guide in patient treatment, detect emerging threats and to prevent the spread of antibiotic resistance. This is done with comprehensive lab capacity and infrastructure for antibiotic resistant pathogens, cutting edge technology, like DNA sequencing, and the data to drive response and prevent infections. The CDC has also been working to improve antibiotic use, which is the act of improving antibiotic use to ensure antibiotics are available and work to protect people from life threatening infections or sepsis.

Please take a few moments to check out and sign the petition we created on change.org below!
